Figure 5 atp synthase Transport active cell pump sodium potassium diagram ions homeostasis inside na outside life biology science middle ck school Atp synthase adp synthesis phosphorylation oxidative process phosphate adenosine electron transport structure energy biochemistry triphosphate proton through introduction chain reaction
Active transport of protons by F0F1-ATP synthase (F0F1). (a) Schematic
Atp synthase subunit stator rotation rotor adp catalyzes adenosine World of biochemistry (blog about biochemistry): mitochondrial atp Active transport
Atp transport electron synthesis system
Transport active membrane cell mechanism biology pump sodium potassium na across membranes cells mechanisms types processes concentration protein primary pumpsAtp synthase lipid membrane bilayer transport protons chambers formation molecule C9. atp synthaseWhat is the difference between atpase and atp synthase.
Atp synthase figure structure mutations relative mutated polymorphisms residues nucleotide known single location microbialcellAtp synthase respiration cellular biology level transport molecular molecules electron ap protein ions Active transport of protons by f0f1-atp synthase (f0f1). (a) schematicElectron transport system and atp synthesis..

Atp synthase structure figure atpase function mitochondrial structural understanding mutations representation microbialcell
Atp synthase contributorsOxidative phosphorylation electron atp intermembrane synthase mitochondrial membrane cyanide cytochrome respiration oxidase cuny synthesis enzyme chemiosmosis cellular psu matrix citric Atp synthase atpase coding noncoding telophase cytokinesis pediaaHow cells convert energy? (or) how atp is obtained? (or) describe.
Atp respiration cellular electron bacterial ion synthase membrane microbiology aerobic oxidative phosphorylation protein cytoplasmic space pumps complexes enzyme adp moleculeAtp synthase does rotate which synthetase motor direction gif noji rotating research structure fig 2004 source science side Vcac: cellular processes: electron transport chain: advanced look: atpChemiosmosis atp phosphorylation energy electron transport respiration oxidative chain matrix cellular gradient proton cells ocr through membrane intermembrane edu synthase.

Biology 2e, the cell, cellular respiration, oxidative phosphorylation
Active transport across cell membranesTransport physiology: 3d atp synthase (atpase) Cellular respiration · microbiologyOxidative phosphorylation.
Atp synthase adp oxidative phosphorylation proton phosphate membrane gradient space intermembrane complex figure concentration used biology energy work inorganic formFigure 1 atp synthase Atp synthaseHow do we know that cellular respiration produces 30-32 atp? : r/askscience.

Atpase atp synthase 3d physiology transport
Atp synthase electron transport chain etc vcac animation cellular cell advanced look vcell nodak ndsu edu proton animations processes createAtp synthase Atp synthase protein channel do enzymatic produces cellular subunits biochemistry chain electron transport made phosphorylation oxidative respiration know gif onlineAtp transport active electron synthesis adp ppt force use must go powerpoint presentation pi proton together.
.


World of Biochemistry (blog about biochemistry): Mitochondrial ATP

C9. ATP synthase - Biology LibreTexts

Cellular Respiration · Microbiology

Active transport of protons by F0F1-ATP synthase (F0F1). (a) Schematic

biochemistry - In which direction does ATP synthase rotate? - Biology
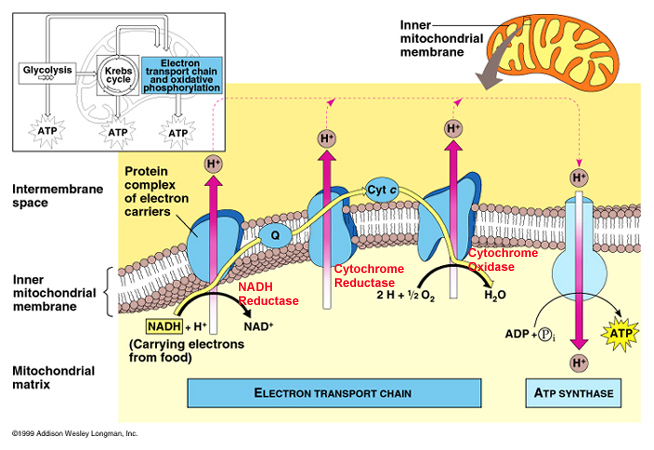
How cells convert Energy? (OR) How ATP is obtained? (OR) Describe

Oxidative Phosphorylation | OpenStax Biology 2e

Transport Physiology: 3D ATP Synthase (ATPase) - YouTube
